Nested if and Multi-Way if-else Statements
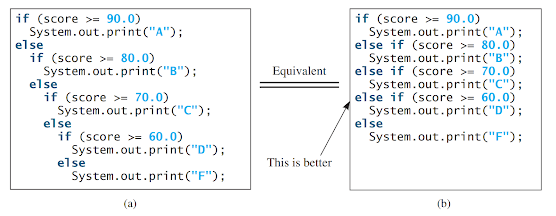
Nested if and Multi-Way if-else Statements: An if statement can be nested inside another if statement, forming a nested if statement. This allows for more complex decision-making in a program. In a nested if statement, an if statement is placed inside another if statement. The inner if statement is considered to be nested within the outer if statement. There is no limit to the depth of nesting and an inner if statement can also contain another if statement. Here is an example of a nested if statement: if (i > k) { if (j > k) System.out.println("i and j are greater than k"); } else { System.out.println("i is less than or equal to k"); } In this example, the inner if statement ` if (j > k) ` is nested inside the outer if statement ` if (i > k) `. This allows for di...


